How to boost creative thinking? Methods and rules of effective brainstorming

Author
Creativity isn’t a natural flair or genetic feature. Nowadays, it’s a valuable skill that can be trained – just like muscles! However, knowledge and techniques are necessary to do the exercises correctly. Brainstorming is one of them in the context of creativity training.
You can obviously go to the gym by yourself, without any training plan or motivation. But you can also engage in a team sport, which, apart from the necessary dose of activity, will ease gaining the desired results as well as deliver a lot of energy and satisfaction. This is how brainstorming works. It’s successfully used in different business and marketing activities.
In this article, you’ll find out
- What is brainstorming? What stages does it consist of?
- What are the most popular methods of brainstorming?
- How to conduct an effective brainstorming session?
How does brainstorming work? Definition and purpose
Brainstorming is a corporate method of solving complex problems and delivering creative solutions through unconventional thinking. Its main purpose is to generate many different ideas, which are evaluated and selected.
Brainstorming sessions are usually a form of meetings that, apart from delivering innovative solutions, are also a great way to integrate the team and build relationships. Apart from its numerous advantages for the team, brainstorming also develops the creative thinking of the individuals and increases their motivation.
In which activities can you use brainstorming? In order to come up with a name for a new product or advertising slogan, a creative agency may conduct a brainstorming session. At Elephate, we can’t imagine the process of creating a digital PR campaign without brainstorming. The techniques of creative thinking can also be used while generating new topics for articles for the company blog.
It’s worth mentioning that brainstorming isn’t exclusive to the creative industry – companies from other fields may also use it! Executives will find help in this technique, e.g. while determining new ways of development for the company. Managers and specialists, on the other hand, may improve the foregoing working patterns or find a way out of the negative situation.
Stages of brainstorming
Although brainstorming is associated with the unlimited generation of ideas, it should be structured in order to be effective and deliver expected results. The process of brainstorming starts by defining the problem, organizing a team, and designating the moderator. It’s important to make sure that every member understands the essence of the issue and the rules of participation in brainstorming. At the preparation stage, you should also choose the methods that will be used during the session.
The next phase is generating ideas, which is the most creative part of the process. Its duration depends on the number of participants and the complexity of the subject – however, it shouldn’t be longer than 30 minutes.
Analysis and ideas evaluation are stages that close brainstorming. On their basis, the team selects the most accurate solution (or solutions) that will be implemented.
Brainstorming – the rules of a creative storming
Gavin Ambrose and Paul Harris mention in their book “Design Thinking” 6 important rules of brainstorming:
It’s the first and the most significant rule of brainstorming. During the creative process, all ideas are important, that’s why you shouldn’t judge and criticize each other. Criticism very often stems from expressing your own opinion and sharing ideas (especially those that are seemingly odd, different, or incomplete). During brainstorming, our activity, creativity, and open-mindedness are all that count.
Brainstorming is generating ideas, not analyzing them – the evaluation stage will come later. Try not to favor or analyze only one solution, but continue the process of generating new concepts.
- Focus on quantity, not quality
To gather as many potential solutions as possible, you may determine a specific numerical goal. It’ll motivate the team and help avoid situations, in which the group will come to a standstill.
Just as with the previously mentioned numerical goals, the set hour of ending the session helps increase the effectiveness of brainstorming, which encourages participants to put thoughts into words faster and generate more ideas.
- Let your imagination run wild
The participants of brainstorming shouldn’t be afraid of proposing unconventional or even crazy ideas. Nonsense often leads to solutions, that make perfect sense! To make it happen, it’s essential to build trust and sense of security within a team.
The person who runs the brainstorming session should encourage all members of the meeting to participate actively and equally. Brainstorming is a team effort – taking advantage of collective creativity, “bouncing” thoughts off each other, and building ideas together lead to the most interesting solutions.

Warm up before brainstorming
If creativity is like a muscle, and brainstorming is a training in creative thinking, you can’t miss a warm-up! Creative exercises, for a start, help participants relax, break the ice, build trust and improve concentration. We often have brainstorming during a busy working day – in this case, the warm-up will let us break away from what we’ve been working on and charge the creative batteries. It’s much easier to start doing more serious challenges with positive energy after simple exercises.
To warm up your brain before starting the session of ideas, you can use the following examples of creative warm-ups.
An alternative purpose of objects
It’s one of the most popular creative warm-ups, which helps train unconventional thinking. In this exercise, we take a closer look at everyday objects and try to find completely different functions for them than they normally have. Within 3 minutes, try to come up with as many new and surprising functions as you can for:
- chair,
- ruler,
- toilet paper,
- socks,
- pan,
- paper clip…
or other “usual” object that comes to your mind. You can group the participants and encourage them to compete for the number of generated ideas.
Bad ideas
It’s not easy to convince people to share stark ideas. An exercise of “bad ideas” helps the team approach the problems with an open mind, encouraging them to consider all possible advantages and purposes of even the craziest ideas.
How to do this exercise? Divide the participants into groups of two or three people. Assign an objectively bad idea to every team, e.g., socks made of sandpaper. Give the groups 5 minutes to discuss the potential advantages and purposes of the particular product. Let every team “sell” their bad idea!
Continued storytelling
Teams in which participants listen to each other and cooperate well during the brainstorming session are able to inspire more and create innovative solutions. This warm-up allows exercising improvisation skills, active listening, and quick thinking. It consists of creating a coherent story by the team in which every participant adds one sentence.
To do the exercise smoothly, choose a simple and general topic (e.g., vacation in Mexico). Start the story with one sentence and give the floor to another person. Every participant has to pay attention to how the story develops in order to add something constructive to the narration when it’s their turn. Continue as long as the story finds a natural ending or everyone says a few sentences.
Warm-up of the humanist
Everyone, who likes word plays, will also like this exercise. The rules are simple: pick a random letter from the alphabet and, within 3 minutes, build the longest sentence, starting every word with this letter. For example: The teacher taught tennis to the tiny tots, taking the time to totally teach them the tricks they thought they took time to train themselves to trump tournaments.
You can modify the warm-up of the humanist a bit by building a sentence in which each word begins with the last letter of the previous word. Example: Darren’s slowworm muddled down never-ending gravel lanes, smiling graciously yet tired.
Filling out the shapes
We also have a proposal for aspiring artists. You’ll need colored pencils or markers and sheets of paper (according to the number of participants) on which they’ll draw and copy a chosen shape, e.g., triangle, square, or circle, in regular gaps. You can easily do this exercise online using a drawing tool, e.g., Jamboard.
Set the timer for 10 minutes. Within this time, draw as many objects, figures, and forms as possible based on a particular shape. You can draw both inside and outside the figure, but you cannot modify it (elongate, cut, extend). As the last step, try to guess together what your “art” represents!
Exemplary methods of brainstorming
When we’re already warmed up and have open minds, we can start the proper brainstorming. You can use many creative methods. That’s why it’s worth considering earlier which one will be the best for the particular case. The selection of the proper brainstorming technique depends on, i.a., the kind of the issue, expected effect, number of participants, or form of the meeting (online vs. offline).
When we meet offline, we have to provide proper space and tools, such as a board or flipchart, colored markers, and sticky notes. During online brainstorming, on the other hand, you will need working devices (cameras, microphones), a good Internet connection, and selected software (e.g., Google board, Jamboard, or spreadsheet).
There are many brainstorming methods – below we discuss 5 exemplary techniques, that are worth trying during creative processes in a group.
Mind map
Mind mapping is a technique that is worth starting the process of creative problem-solving with. A well-constructed mind map not only emphasizes important facts, but also allows for highlighting the structure of a particular topic and discovering interesting connections between seemingly distant ideas.
How to create your own mind map, though? In the center of the board (flipchart, paper, or screen) write down a main idea/slogan – it’ll be the center of your mind map. Next, add an unlimited number of the connected strands, coloring them adequately. Remember to keep the hierarchy of the terms. Ideas should be connected with lines, creating a net of relations that is clear and easy to understand at first sight.
6-3-5 method (brainwriting)
What does this variant of brainstorming consist of? 6 participants, who take part in it, have to write down 3 ideas on paper or a dedicated spreadsheet in 5 minutes. Next, the members of the team swap the sheets, passing them to the next person. As a result, after 6 rounds (which is 30 minutes), we have 108 generated ideas! Of course, you can adjust brainwriting to the number of participants (e.g., in a group of 4, we use the 4-3-5 method etc.).
The enormous advantage of this method is how easily you can engage all participants of the creativity session on an equal level. Its purpose allows avoiding situations where introverts would be dominated by louder people – thanks to the anonymity and writing form, every team member may feel comfortable in expressing their own ideas. Additionally, brainwriting allows for deriving inspiration from the rest of the participants – before we add other ideas to the received list, we can read the previous ones and propose something new.
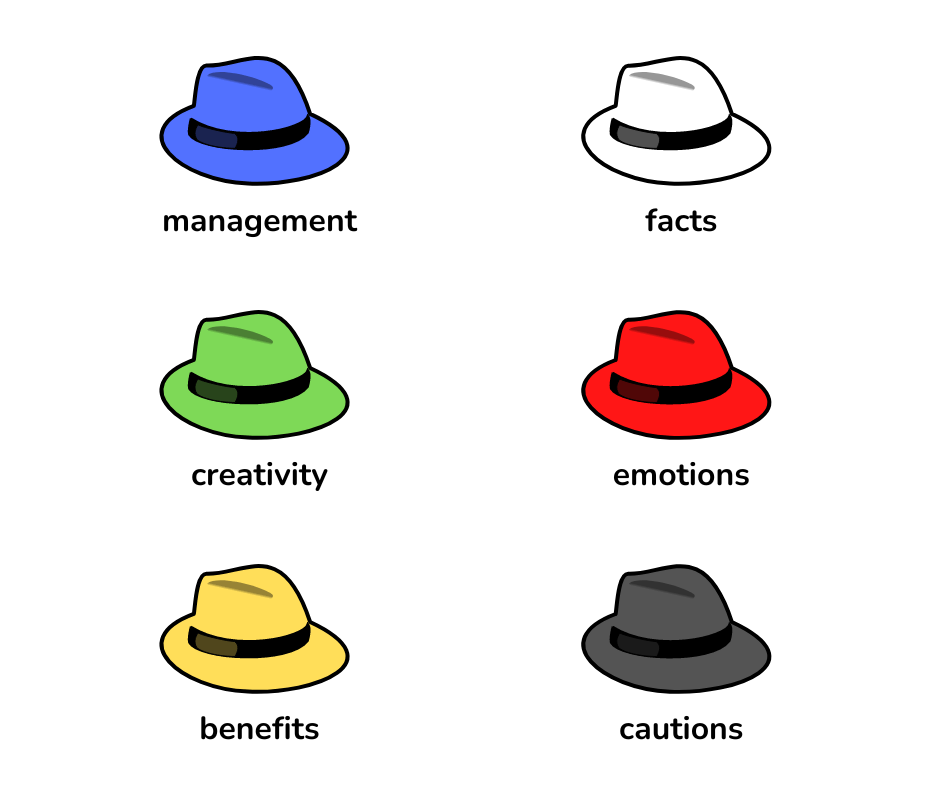
Six thinking hats
Difficulties in making a decision may often stem from a mess of thoughts. The six thinking hats method organizes the thinking process and helps separate emotions from information, logic, expectations, hopes, ideas, and creativity – they’re all represented by the hats, which are the ways of looking at the problem.
The six thinking hats method consists of six participants playing different roles, which allows analyzing the issue from different angles and finding new ideas. What does it look like in practice? Before starting the discussion, determine its topic and the expected result, as well as the moderator of brainstorming (blue hat). Then, the team members should present the facts about the discussed issue (white hat). Next, it’s time for generating the ideas (green hat) and their evaluation (yellow hat – advantages, black hat – disadvantages). At this moment, you can express your emotions and feelings about the problem and proposed solutions (red hat). Finally, the moderator sums up the discussion and formulates conclusions.
5 Whys method
5 Whys is a technique that allows finding the cause of the problem. Its rules are very simple: when there’s an issue, we try to get to its primary cause, asking 5 times “Why?”. When we finally find the source of the disruption, we can thoroughly look into its cause and focus on finding an effective solution (as well as preventing from causing the problem again).
Reverse brainstorming
OReverse brainstorming is based on the natural human skill of easily looking for problems rather than solutions. In contrast with classical brainstorming, where the goal is to find the solution to the difficulty, in the reverse version we take a look at issues that can make it more difficult or impossible to solve. This way, we can predict the potential failures and identify the causes of the ongoing problems.
The process of reverse brainstorming may run as follows:
- introducing the problem,
- looking for the causes and other potential issues,
- gathering ideas,
- reversing the gathered ideas.
This method may also be useful as a warm-up before starting the creative process, especially in groups dominated by analytical minds.
Evaluation of ideas
Generating hundreds of ideas is just midway – the key to the success is their analysis and selection. In order to evaluate the generated solutions, you need criteria to analyze them. They can contain, a.i., required resources, costs, time factors, ease of implementation, or adjustments to the goal – you decide which will be essential in your case. For every selected indicator, you can use the scale, e.g., from 1 to 5, or simply “yes/no” indicating which criteria were fulfilled.
Such a way of evaluation allows organizing ideas and eliminating weaker or undoable solutions (which could be in favor during brainstorming!).
Reuse of the six thinking hats method
You can also use the six thinking hats method to evaluate gathered ideas. Even if we used a different method to generate ideas, nothing stands in the way to wear a yellow hat (discussing the advantages of the particular solutions), a black hat (listing their disadvantages), and a red hat (expressing your emotions about the proposed ideas).
Voting
If after the analysis and evaluation of ideas there are still some favorites, you can take a vote among the participants of brainstorming. Let them indicate one or two favorite solutions and justify their choice.
Evaluation by a different team
You can also appoint another team to carry out the evaluation of the proposed ideas. The assessment team will be able to analyze the solutions objectively because none of the members took part in brainstorming. It’s vital that these people also know the issue and organization in question.
***
Brainstorming is like a set of exercises that start creative thinking. Do the training regularly to keep in shape at a high level, and change the techniques if you’re worried about the routine and fall of creativity. Remember that you can freely use the available methods and work out your own, which will be the best in your environment, industry, or team.
Sources:
Basics Design 08: Design Thinking by Gavin Ambrose and Paul Harris
https://lucidspark.com/blog/brainstorming-warm-up-exercises
https://aniakania.com/2018/01/06/rozgrzewka-mozgu/